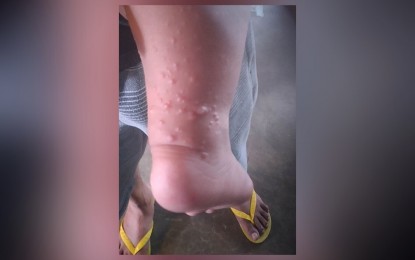
OUTBREAK. Blistering is one of the symptoms of the highly-contagious hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD). The disease has already affected 33 villages in Borongan City, Eastern Samar province, prompting the city government to declare an outbreak. (PNA file photo)
TACLOBAN CITY – The hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) has already affected 33 villages in Borongan City, Eastern Samar province prompting the city government to declare an outbreak.
The number of HFMD-affected persons rose to 154 on March 10 -- the day the city declared an outbreak-- from just 95 cases two days earlier, according to a report from the city epidemiology and surveillance unit.
"Communities and the general public must comply with minimum public health standards and non-pharmaceutical interventions as may be enforced for diseases spread by droplets and direct contact," said Daisy Sacmar, city health office chief, in a statement Monday.
The 33 affected villages are Taboc, Cabong, Campesao, Canlaray, Tabunan, Cabalagnan, Purok District 1, Bato, Lalawigan, Balud, Sta. Fe, Ando, Bugas, Songco, Libuton, Hindang, San Mateo, Maypangdan, San Saturnino, Calingatngan, Calico-an, Can-abong, Canjaway, Purok A, Sabang North, Amantacop, Bayobay, San Jose, Tamoso, Purok H, Purok G, San Gabriel and Purok District 2.
The affected barangays are more than half of the city's total 61 villages.
HFMD is a highly contagious viral disease often affecting infants and children.
Most HFMD cases are mild, self-limiting, and non-fatal, but may progress to meningitis, encephalitis, and polio-like paralysis if left unmanaged.
This disease is usually transmissible through contact with nose and throat discharges, the saliva of infected persons, and/or contaminated objects and cannot be contracted from animals.
Among the signs and symptoms of HFMD are fever; sore throat; feeling of being unwell (malaise); painful, red, blister-like lesions on the tongue, gums, and insides of the cheeks; red rash, without itching, but sometimes with blistering on the palms, soles, or the buttocks; irritability in infants and toddlers; and loss of appetite.
The public is asked to observe minimum public health standards, such as physical distancing and using appropriate personal protective equipment, especially when symptoms are present, such as properly fitted face masks and gloves.
If symptoms persist beyond 10 days, patients are advised to seek medical consultation immediately, most especially if the symptoms become severe, or are accompanied by the nervous system and cardiorespiratory signs and symptoms. (PNA)
